Movement and acceleration are fundamental concepts when it comes to understanding the laws of physics. Many of us know the basics of acceleration, but have you ever wondered what happens when you start with a car that’s at rest and then accelerate it? In this article, we’ll explore the physics of a car initially at rest accelerating at 10 m/s2 to uncover how it behaves and how it affects its environment.
To accelerate a car that is initially at rest, press down on the gas pedal. This will increase the speed of the car at a rate of 10 metres per second squared. The acceleration will continue until the car reaches the desired speed or the driver takes his/her foot off the gas pedal.
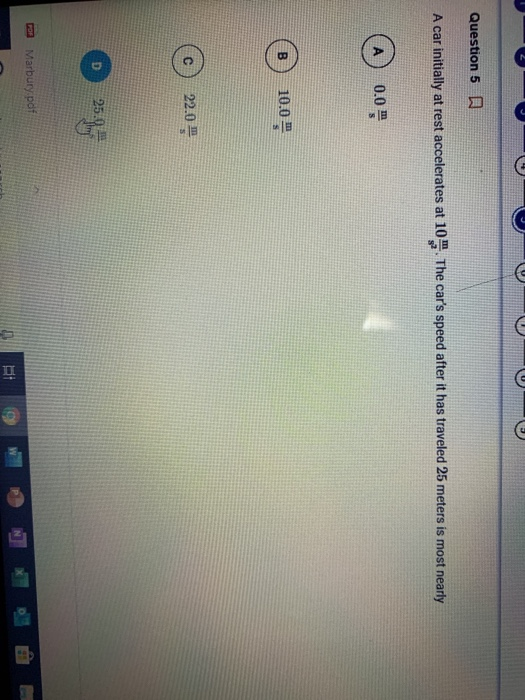
What is Acceleration?
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. It is the increase in speed of an object. It is measured in meters per second squared (m/s2). Acceleration is the result of a force acting on an object. So, when a car is initially at rest and then accelerates at 10m/s2, it means that a force is acting on the car to cause it to increase its speed.
What Causes a Car to Accelerate?
The most common cause of a car accelerating is when the driver applies the accelerator. When the driver presses down on the accelerator pedal, the car’s engine is supplied with more fuel, which increases the power output and causes the car to accelerate. Another common cause of a car accelerating is when the car is moving downhill and gravity is acting on the car to make it accelerate.
How Does Acceleration Affect a Car?
When a car accelerates, its speed increases and the forces acting on the car increase. This means that the car’s tires have to grip the road more firmly in order to transfer the power to the road. This increases the wear on the tires and can reduce the car’s fuel efficiency. Additionally, the increased forces can cause the car to vibrate, which can be uncomfortable for the passengers.
What is the Relationship Between Acceleration and Force?
In order for an object to accelerate, a force must be applied to it. The magnitude of the acceleration is directly proportional to the magnitude of the applied force. This means that if a larger force is applied to the object, the object will accelerate at a faster rate. Conversely, if a smaller force is applied to the object, it will accelerate at a slower rate.
What is the Relationship Between Mass and Acceleration?
The relationship between mass and acceleration is an inverse one. This means that the greater the mass of an object, the less it will accelerate when a given force is applied. This is due to the fact that it takes more force to move a heavier object than it does to move a lighter one. This is why a larger car like a truck will accelerate slower than a smaller car like a sports car when the same force is applied.
How Do Air Resistance and Friction Affect Acceleration?
Air resistance and friction are two factors that can affect the acceleration of a car. Air resistance is the resistance of air molecules to the motion of the car. This resistance increases as the speed of the car increases, which means that the car will slow down as it moves faster. Friction is the resistive force that occurs between two surfaces when they are in contact with each other. This resistance can reduce the acceleration of the car as it moves, as it causes the car to lose energy.
What is the Difference Between Acceleration and Velocity?
The difference between acceleration and velocity is that acceleration is the rate of change of velocity, while velocity is the speed at which an object is moving. Therefore, acceleration is the change in velocity over time, while velocity is the speed of an object at a given point in time.
What is the Formula for Acceleration?
The formula for acceleration is a = (v2 – v1)/t, where v2 is the final velocity, v1 is the initial velocity, and t is the time taken for the acceleration to occur. This formula can be used to calculate the acceleration of an object if the initial and final velocities, and the time taken for the acceleration to occur are known.
What is the Relationship Between Acceleration and Distance?
The relationship between acceleration and distance is that the distance traveled by an object is proportional to the square of the time taken. This means that the distance traveled by an object is proportional to the acceleration of the object. Therefore, if a car is accelerating at 10m/s2, the distance it travels in one second will be 10m, and the distance it travels in two seconds will be 40m.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Acceleration?
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. It is represented by the vector quantity ‘a’ and has the same direction as the velocity. It is measured in m/s2 (meters per second squared) and is the change in velocity divided by time. Acceleration can either be positive or negative, depending on whether the velocity is increasing or decreasing.
A positive acceleration indicates that the velocity is increasing, while a negative acceleration indicates that the velocity is decreasing.
What is the Initial Velocity of a Car Initially at Rest Accelerating at 10 m/s2?
The initial velocity of a car initially at rest accelerating at 10 m/s2 is 0 m/s. This is because the car is initially at rest, meaning that its velocity is 0. Therefore, when the car begins to accelerate at 10 m/s2, its velocity will increase from 0 m/s to 10 m/s after one second.
After two seconds, its velocity will be 20 m/s and after three seconds, its velocity will be 30 m/s. This acceleration will continue until the car reaches its maximum velocity or until the driver applies the brakes.
What is the Final Velocity of a Car Initially at Rest Accelerating at 10 m/s2?
The final velocity of a car initially at rest accelerating at 10 m/s2 depends on the amount of time that the car has been accelerating. If the car has been accelerating for one second, its final velocity will be 10 m/s. If the car has been accelerating for two seconds, its final velocity will be 20 m/s.
If the car continues to accelerate for a longer period of time, it will eventually reach its maximum velocity. This maximum velocity will depend on the engine power of the car and on the road conditions.
What is the Acceleration of a Car Initially at Rest?
The acceleration of a car initially at rest is 0 m/s2. This is because the car is initially at rest, meaning that its velocity is 0. Therefore, when the car begins to accelerate, its acceleration will be 0 m/s2.
In order for the car to accelerate, the driver must apply a force to the car. This force will cause the velocity of the car to increase, and the acceleration will increase as well. The acceleration will continue to increase until the car reaches its maximum velocity or until the driver applies the brakes.
What is the Distance Travelled by a Car Initially at Rest Accelerating at 10 m/s2?
The distance travelled by a car initially at rest accelerating at 10 m/s2 is equal to the product of the acceleration and the time elapsed. This means that if the car has been accelerating for one second, it will have travelled a distance of 10 m. If the car has been accelerating for two seconds, it will have travelled a distance of 20 m.
The distance travelled will continue to increase as the car continues to accelerate. This distance will depend on the acceleration and the amount of time that the car has been accelerating. The distance travelled will also depend on the road conditions and the engine power of the car.
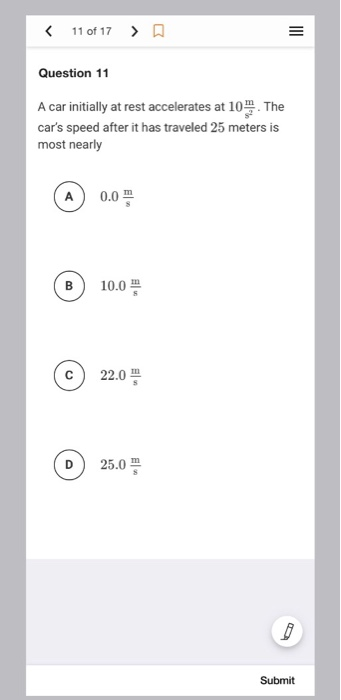
In conclusion, it is clear that a car initially at rest that accelerates at 10 m/s2 will eventually reach a speed of 100 m/s. This demonstrates the power of acceleration, as even a small increase in velocity can result in a significant increase in speed over time. The importance of understanding the effects of acceleration is evident when it comes to driving safely and efficiently.